 |
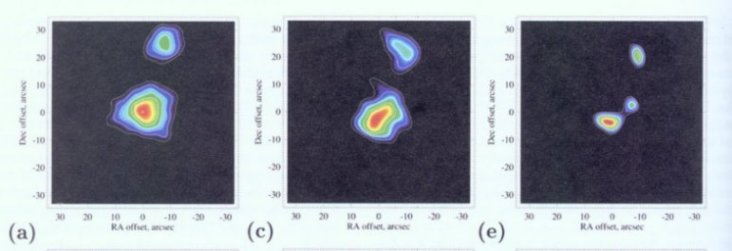
| Three far infrared images of Eta Corvi spread from left to right with increasing resolved detail. The star itself is not visible. Instead we see heat radiation from a dusty disk (at center) with a diameter more than 200 times the distance between Earth and Sun. (The radiating source toward the top is in the background and is not relevant.) At far right the disk is seen to break into a pair of blobs that lie opposite the unseen star and that may indicate the presence of a Neptune-like planet. (From a paper by M. C. Wyatt, J. S. Greaves, W. R. F. Dent, and I. M. Coulson in the Astrophysical Journal, vol. 620, p. 492, 2005.) |